Electronic Industries
The electronics industry is the economic sector that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices built-in automated or semi-automated factories operated by the industry.
.jpg)
Electroless Nickel Line
Electroless nickel plating is also known as chemical or autocatalytic nickel plating. The process uses chemical nickel plating baths. The most common electroless nickel is deposited by the catalytic reduction of nickel ions with sodium hypophosphite in acid baths at pH 4.5–5.0 at a temperature of 85–95°C.

Cadmium Plating Line
Modern electroplating is a form of metal finishing used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, military, medical, RF microwave, space, electronics and battery manufacturing. It is the electrochemical process whereby metal ions in solution are bonded to a metal substrate via electrodeposition.
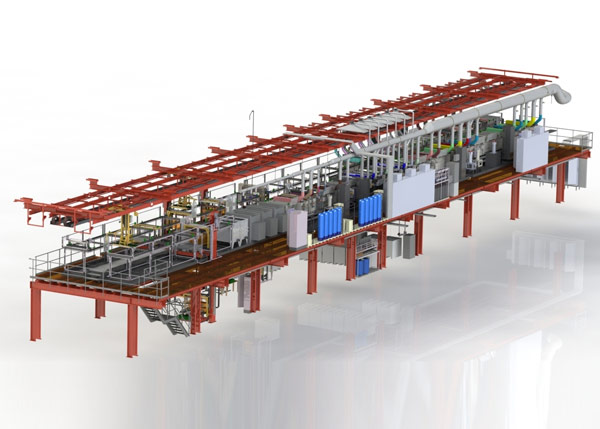
Zinc-Nickel Plating Line
Zinc-nickel plating is an environmentally and safer alternative to cadmium and can be used across a wide range of industries. It combines the sacrificial coating properties of zinc with the strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance of nickel – creating a surface finish that, in some cases, is superior to cadmium.
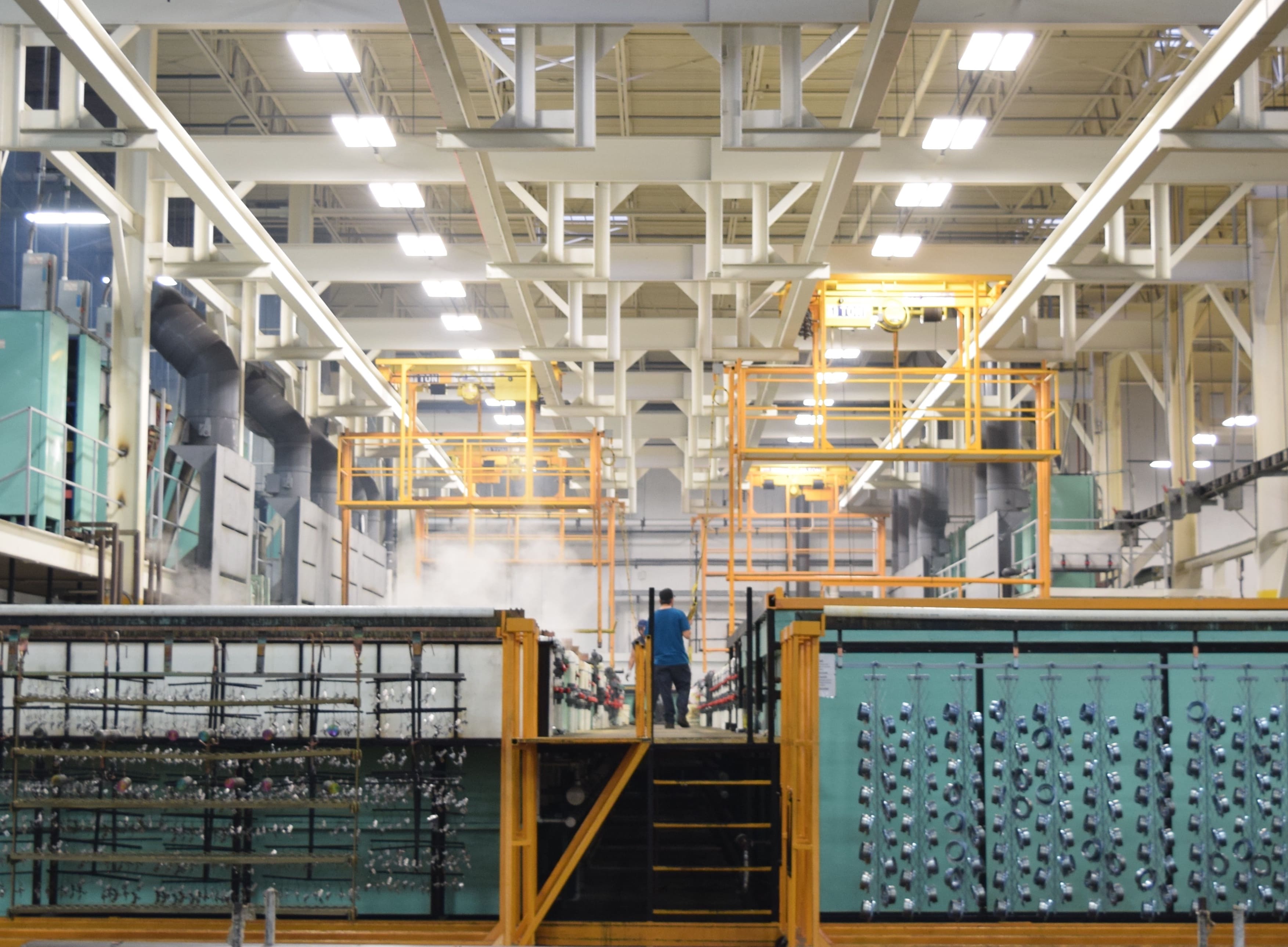

Zinc Cobalt Plating Line
Zinc Cobalt process produces a tough, durable finish with excellent lubricity and greater resistance to seizure, essential for moving parts and threaded connections. Lower toxicity of the process and the deposit makes the coating safer all round than cadmium.
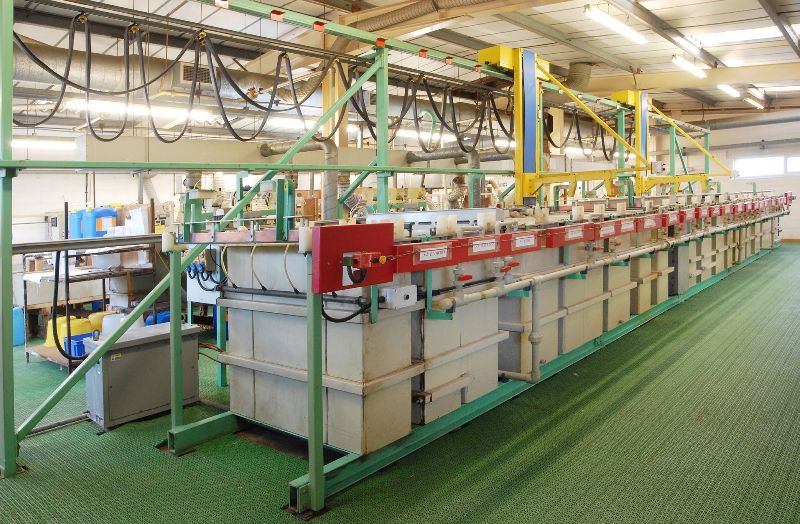

Silver Plating Line
The silver plating of copper will increase the operating temperature of copper alloy conductors. Silver also provides superior solderability and excellent electrical conductivity. When used for plating a copper conductor, silver will enhance the high-frequency transmission capabilities of the wire.

Gold /Ruthenium Plating Line
This metal provides an inert finish that protects against corrosion, is bondable, provides high hardness and is conductive. With quality plating, it can produce a pore-free, mirror-like finish. The benefits of ruthenium electroplating make it an ideal metal for numerous industrial applications.

.jpg)
.jpeg) D Square Electroplating Machines Pvt. Ltd.
D Square Electroplating Machines Pvt. Ltd. 







